Working of Institutions Class 9 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the three organs of the Government?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Executive
- Legislative
- Judiciary
Question 2.
Who is the head of the state and the head of the government?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The President is the head of the state whereas Prime Minister is the head of the government
Question 3.
What is a Parliament? Name the two houses of the Parliament?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
It is the supreme law making body of India. It has two Houses
Question 4.
What are institutions?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
The arrangements which are made in modern democracies to run the government
Question 5.
Name any three institutions responsible to run the democratic government in India?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- The Prime Minister and the Cabinet
- The Civil Servant
- The Supreme Court
Question 6.
Name the institution where disputes between citizens and the government are finally settled?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Supreme Court
Question 7.
Why democratic governments insist on institutions? Give two reasons?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Institutions involve rules and regulations
- Institutions bind the hands of the rulers as these involve meetings, committees and routines
Question 8.
Which House has more power regarding the money bill? Give reason?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Lok Sabha exercises more powers in money matters. Once the Lok Sabha passes the budget of any other money related law, the Rajya Sabha cannot reject it. The Rajya Sabha can only delay it by 14 days or suggest changes, in it. The Lok Sabha may or may not accept these changes
Question 9.
Explain No Confidence Motion?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
Only a person who enjoys the support of the majority of the members of the Lok Sabha is appointed as the Prime Minister. If a no confidence motion is moved in the Lok Sabha, and passed, then,the Government has to resign
Question 10.
With reference to the Rajya Sabha answer the following questions?
Year of Question :(2014)
- (i) What is its power relating to money bill
- (ii) Can it pass a No-Confidence Motion
Answer:
- (i) A Money bill can originate only in the Lok Sabha. When it is sent to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot reject it. The Rajya Sabha can delay it for 14 days
- (ii) No, Rajya Sabha cannot pass the No-confidence Motion
Question 11.
Define Executive?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
At different levels of any government we find functionaries who take day-to-day decisions, but do not exercise the supreme power on behalf of the people. All those functionaries are collectively known as the executive
Question 12.
Who appoints the Prime Minister?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Prime Minister is appointed by the President
Question 13.
What is the tenure of the Prime Minister?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Prime Minister does not have a fixed tenure. Normally a Prime Minister is elected for 5 years, but remains in power till he enjoys the majority support
Question 14.
Who are Cabinet Ministers?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
They are usually the top level leaders of the ruling party or parties, who are in charge of the major ministries like Defence, Railway, Foreign Affairs etc. Normally, all the major decisions are taken by these ministers
Question 15.
What is judiciary?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
All the courts at different levels in a country are called the judiciary
Question 16.
Which is the highest court of India?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Supreme Court
Question 17.
"The Constitution of India has made necessary provisions for ensuring independence of judiciary." Justify your answer by giving two reasons?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- The judges are appointed by the executive on the basis of the prescribed qualifications, and according to a well established procedure
- The Judges cannot be removed at the whims of the executive
Question 18.
Who appoints the Chief Justice of India and the other judges?
Year of Question :(2013)
Answer:
The President of India appoints the Chief Justice of India. The President consults other Judges of the Supreme Court and the High Courts while making appointments of other judges
Question 19.
State any two powers of the Supreme Court of India?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- The Supreme Court acts as the guardian of fundamental rights
- It acts as a guardian of the Constitution
Question 20.
What is the composition of Indian judiciary?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- The Supreme Court.
- The High Court.
- The District Court
Working of Institutions Class 9 Important Questions Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is there a need for political institutions?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
- To take decisions : Countries need political institutions to take decisions regarding the welfare of the people. Institutions formulate various policies and programmes
- Implementation : The decisions which have been taken are to be implemented. So countries need institutions to implement the decisions
- To solve the disputes : Institutions are also needed to solve the disputes between various institutions
- To take right decisions : Institutions help the governments to take the right decisions
Question 2.
Distinguish between political executive and permanent executive?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
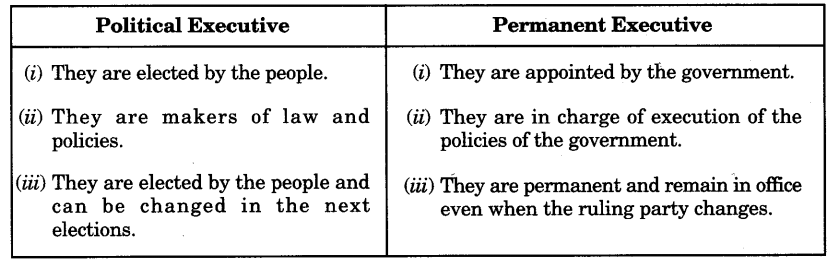
Question 3.
Compare the power, tenure and working of both the Houses of the Indian Parliament.?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
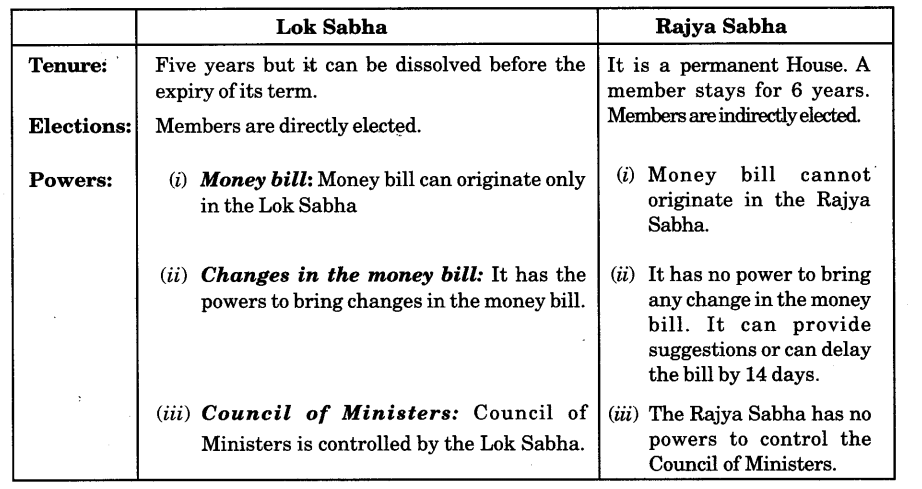
Question 4.
Why do the political executives have more power than the permanent executives?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- In a democracy, the will of the people is supreme, and the political executive is elected by the people
- All the political executives are answerable to the people. The people can change them if they dont work according to the wishes of the people
- The non-political executives are the experts in their field but political executives have to see the welfare of all
- The experts can tell the route, but the political executives have a larger view so they decide the destination
Working of Institutions Class 9 Important Questions Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the major powers and functions of the Prime Minister?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Link : The Prime Minister is the link between the Cabinet and the President. The decisions of the Cabinet are conveyed to the President through the Prime Minister. It is he who keeps him informed on all matters of government
- Formation of the Cabinet: The Prime Minister prepares the list of his Council of Ministers and sends it to the President. He can reshuffle hi? Council of Ministers whenever he likes. He can also ask any minister to resign if he is not satisfied with his working
- Leader of the Lok Sabha : The Prime Minister presides over the meetings of the Cabinet. He maintains co-ordination between different departments of the government
- Foreign Affairs : The Prime Minister plays an important role in the management of foreign affairs. He formulates the internal and external policies of the country
- Leader of the Party: The Prime Minister has the main say in framing the policy of his party
- Leader of the Nation: The Prime Minister is the most important leader of the nation. People always eagerly hear his views. His views related to any internal or external policy are heard more carefully
Question 2.
Explain the major powers and functions of the Parliament?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Legislative Powers : The Parliament can make laws on all those subjects which have been given in the Union List and the Concurrent List. Under certain cases, it can also make laws on those subjects which have been given in the State List
- Control over Finance : The annual budget of the Central Government is passed by Parliament. Without Parliaments approval, the government cannot impose any tax or incur any expenditure
- Control over the Executive: The Parliament can seek information regarding administration. It can pass a resolution of no confidence against the ministry and ask it to resign. Question hours are also quite effective in keeping the government and its ministers under control
- Amendment or New Law : No amendment can be made in the Constitution without the approval of the Parliament
- Functions related to Elections : The Parliament elects the President, the Vice-President, Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Deputy Speaker. Members of the Rajya Sabha elect the Vice-Chairman
Question 3.
Explain briefly the powers and functions of the Supreme Court?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Original Jurisdiction : The original jurisdiction extends to those cases which the Supreme Court has the authority to hear and decide in the first instance
- Between citizens of the country
- Between citizens and government
- Between two or more state governments; and
- Between governments at the union and state level
- Appellate Jurisdiction: It is the highest court of appel in civil and criminal cases. It can hear appeals against the decisions of the High Courts
- Advisory Jurisdiction : As the highest court in the country, the Supreme Court gives legal advice to the President of India on any legal or constitutional matter referred to it. However, the advice is not binding on the Supreme Court
- Guardian of the Constitution: The Supreme Court acts as the guardian and final interpreter of the Constitution. If the government passes any law or issues any order which is in violation of the Constitution, the Supreme Court has the power to declare the law or order unconstitutional
- Guardian of Fundamental Rights: The Supreme Court also acts as a guardian of the fundamental rights of the citizens. When a fundamental right of any citizen is violated by the government or any individual he can seek the protection of the Supreme Court
Working of Institutions Class 9 Important Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots) Questions
Question 1.
Explain the composition of the Council of Ministers?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The Council of Ministers is a large body, it consists all the three ranks of ministers. The Council of Ministers comprises of the three categories of ministers. These are
- Cabinet Ministers : Constitute the inner ring of the council of ministers. These are the top-level leaders of the ruling party / parties who are incharge of the important ministries. They usually meet to take decisions in the name of the council of ministers
- Ministers of State with Independent Charge : They are usually in charge of smaller ministries. They participate in the cabinet meetings only when they are invited
- Ministers of State : They are attached to and are required to assist the Cabinet ministers
Question 2.
Give any three functions (or responsibilities) of the government?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
- Government collects taxes and uses it for administration, defence and development programmes
- Government ensures security to the citizens and provides facilities for education and health
- It formulates and implements several welfare schemes
Question 3.
What is public interest litigation? What is its importance?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:Any one can approach the courts if public interest is hurt by the actions of government. This is called the public interest litigation. The courts intervene to prevent the misuse of the governments power to make decisions. They check the malpractices on the part of public officials
Question 4.
What is job reservation? What is its importance?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
Under job reservation policy some percentage of total government job vacancies are reserved for people and communities who are economically or socially backward. Job reservation policy give a fair opportunity to those communities who so far had not adequately been represented in government employment
Working of Institutions Class 9 Important Questions Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Mention the ethical values which are reflected by the coalition governmen?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- Accommodating different groups and factions
- Alliance
- Interdependence
- Cooperation
Question 2.
Under what circumstances does the President exercise his discretion in the appointment of the Prime Minister?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
With no single party getting a clear majority, a coalition of parties stake their claim to form the government. The President has to use his individual judgement and invite such a leader to head the government as Prime Minister, who can provide a stable government to the country
Question 3.
Why is there a need for political institutions?
Year of Question :(2015)
Or
Why are political institutions important? Give any three points.[CBSE March 2011]
Answer:
- To take decisions : Countries need political institutions to take decisions regarding the welfare of the people. Institutions formulate various policies and programmes
- Implementation : The decisions which have been taken are to be implemented. So countries need institutions to implement the decisions
- To solve the disputes : Institutions are also needed to solve the disputes between various institutions
- To take right decisions : Institutions help the governments to take the right decisions
- To avoid bad decisions : Institutions follow a proper procedure to take decisions. Institutions make it difficult to have a good decision taken very quickly but they also make it equally difficult to rush through a bad decision